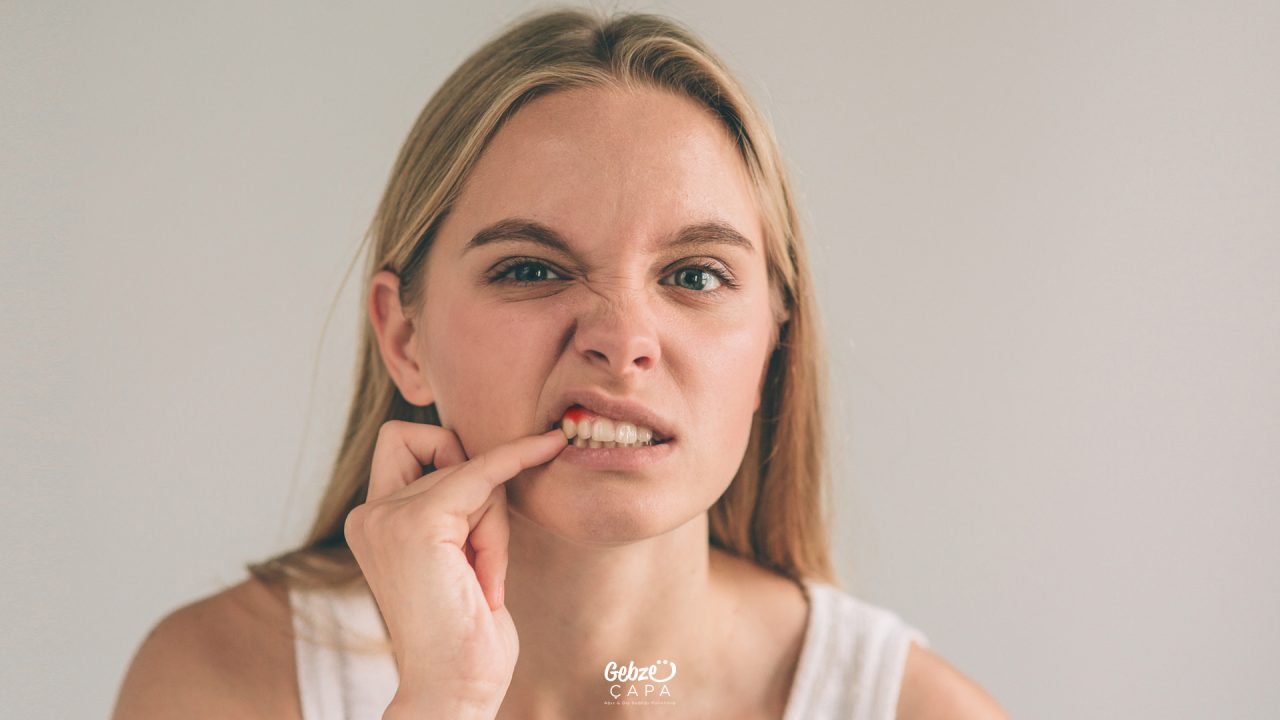
Persistent Gum Inflammation
Dental health constitutes a crucial part of our overall well-being, and gum inflammation is a common issue that can disrupt this balance. This article will comprehensively explore the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment methods of gum inflammation. By providing essential information on dealing with persistent gum inflammation, we aim to guide our valued readers through the necessary knowledge to address this concern.
What is Gum Inflammation and What Are Its Causes?
Gum inflammation, a common oral health issue, occurs as a result of the inflammation of the gums. There are various reasons for gum inflammation, often linked to poor oral hygiene practices. Here is a detailed explanation outlining the primary causes of gum inflammation:
- Accumulation of Plaque and Tartar: Bacteria accumulating as plaque on the teeth can harden over time, turning into tartar. This condition can lead to inflammation when it comes into contact with the gums. Plaque and tartar accumulate in the absence of regular brushing and flossing, significantly impacting gum health.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause in women, can contribute to gum inflammation. Hormonal fluctuations may increase sensitivity in the gums and trigger inflammation.
- Smoking: Smoking is a habit that negatively affects oral health. Smokers are at an increased risk of gum inflammation. Chemicals present in cigarettes can reduce blood circulation in the gums and weaken the immune system, creating a favorable environment for inflammation.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a condition characterized by uncontrolled sugar levels in the body. This can expedite the progression of gum inflammation. Individuals with diabetes should pay extra attention to their gum health.
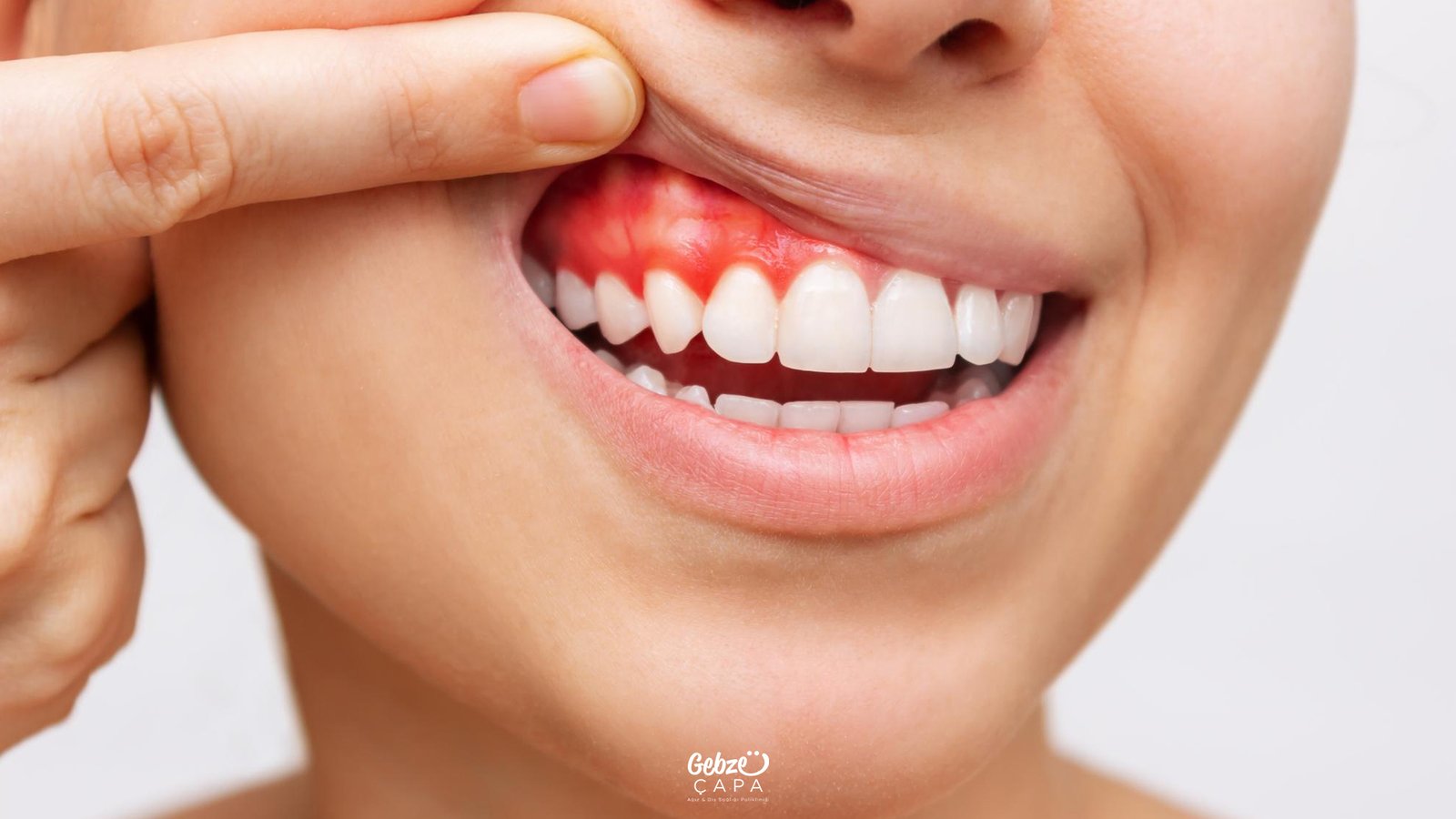
- Incorrect Dental Care: Using the wrong toothbrush or employing an improper toothbrushing technique can lead to gum inflammation. Brushing too forcefully or neglecting the use of dental floss can cause injuries to the gums, paving the way for inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of gum problems may be more susceptible to gum inflammation due to genetic predisposition.
- Poor Dietary Habits: Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, especially a lack of vitamin C, can adversely affect gum health. Imbalanced nutrition can weaken the body’s immune system, increasing the risk of gum inflammation.
Treatment Methods
- Professional Dental Cleaning: One of the fundamental steps in treating gum inflammation is professional dental cleaning. Your dentist contributes to the health of your gums by removing dental plaque and tartar. This procedure also cleans bacteria accumulated in the depths of gum pockets, preventing the spread of infection.
- Antibiotic Treatment: In cases of gum inflammation caused by a bacterial infection, your dentist may prescribe appropriate antibiotics. Antibiotics can help control the infection and contribute to the regression of inflammation. However, it is crucial to use antibiotics in the correct dosage and duration.
- Gum Surgery: In advanced cases of gum inflammation, gum surgery may be necessary. Surgical intervention involves cleaning inflamed tissues, correcting gum contours, and preserving tooth roots to create a healthy environment. Gum surgery is an effective treatment method for advanced cases.
- Oral Hygiene Education: An essential step in the treatment of gum inflammation is oral hygiene education. Your dentist can help ensure regular at-home care by teaching proper toothbrushing and flossing techniques. This helps prevent the recurrence of inflammation.
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet can strengthen the body’s immune system and enhance resistance against gum inflammation. Foods rich in vitamin C and antioxidants support gum health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and managing stress are crucial, as these factors can trigger gum inflammation.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular dental check-ups play a significant role in the treatment of gum inflammation. Your dentist monitors the progression of inflammation and intervenes at an early stage to prevent further complications.

Conclusion
Persistent gum inflammation, when neglected, can lead to serious dental health issues. However, with the right treatment methods and precautions, this problem can be overcome. The treatment of gum inflammation involves individuals maintaining regular dental care and seeking professional assistance.
Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to detect signs of inflammation early and create an appropriate treatment plan. Professional dental cleaning helps keep the gums healthy by removing dental plaque and tartar. This process also educates the patient on proper toothbrushing and flossing techniques.
Antibiotic treatment can assist in controlling bacterial infections. Gum surgery is an effective option for advanced cases, involving the removal of inflamed tissues and restructuring of the gums to create a healthy environment.
Oral hygiene education helps prevent the recurrence of inflammation by instilling proper care habits at home. A healthy diet and lifestyle changes play a crucial role in controlling gum inflammation.
It is essential to remember that dental health is directly connected to our overall well-being. Measures taken against gum inflammation positively impact not only our oral health but also our general health. Our experienced dentists at the dental clinic take pleasure in providing patients with a healthy smile using modern treatment methods. Remember, regular dental care is the most effective way to prevent future dental issues.


