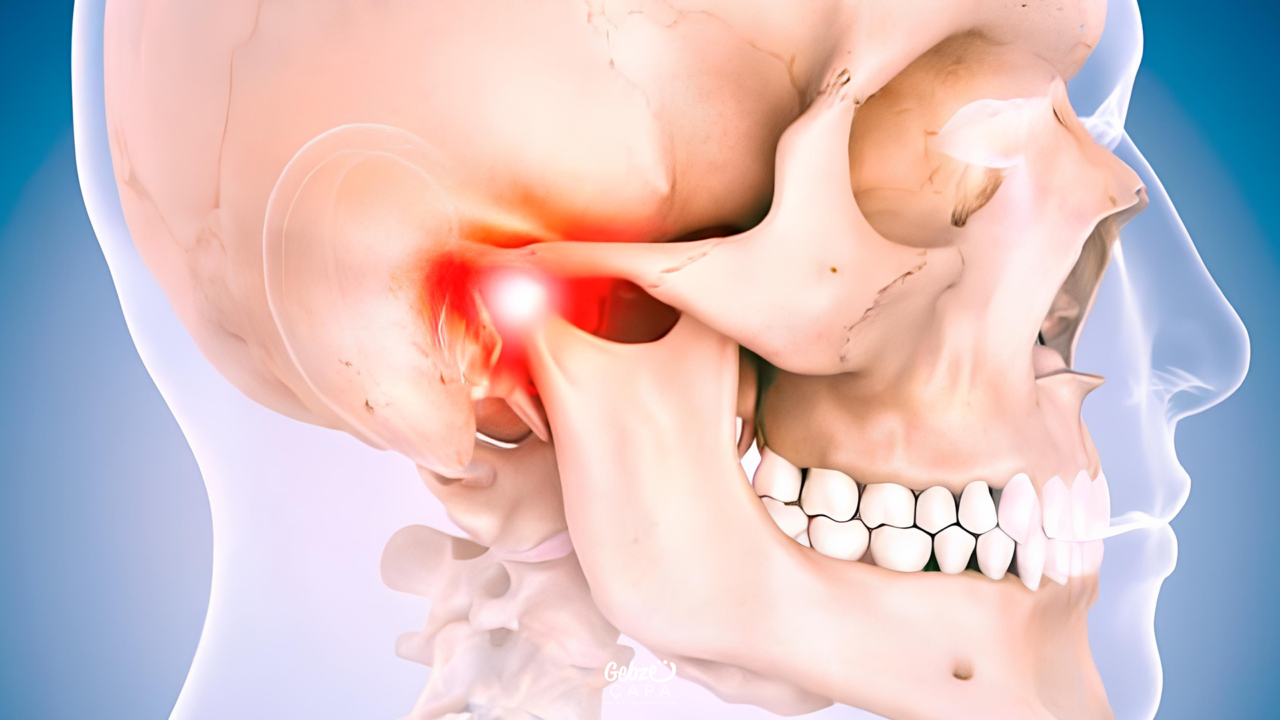
Jaw Joint Pain
The jaw joint, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) as it is medically known, is one of the most complex joints in the human body. This joint is located between the skull and lower jawbone and allows the jaw to move. It plays a critical role in performing basic functions such as speaking, chewing and swallowing in daily life.
TMJ is a joint that can perform both rotational movements like a hinge and sliding movements. Thanks to this feature, the jaw can operate in a wide range of motion, which makes various activities possible. However, the jaw joint can sometimes experience problems for various reasons. These problems may manifest as symptoms such as jaw pain, cartilage damage, or locking during chewing.
Jaw joint health is an important part of overall oral health and should be monitored with regular dentist checkups. In this blog post, we will discuss topics such as jaw joint anatomy, functions, possible problems and treatment methods for these problems in detail. A healthy jaw joint contributes significantly to the overall quality of life and therefore regular care and precautions are important.
Jaw Joint Pain
Jaw joint pain is a discomfort and pain that is usually felt during jaw movements or while at rest. This pain can be a symptom of several conditions known as temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD). TMD refers to a set of disorders that can occur in the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, ligaments, or other structures.
Jaw joint pain can negatively impact an individual’s daily activities. For example, even simple actions such as chewing, speaking, or even making facial expressions can cause pain. Additionally, the causes of jaw joint pain are often very diverse and can vary from person to person. These may include jaw joint trauma, poor dentition, excessive jaw use, stress, and even genetic factors in some cases.
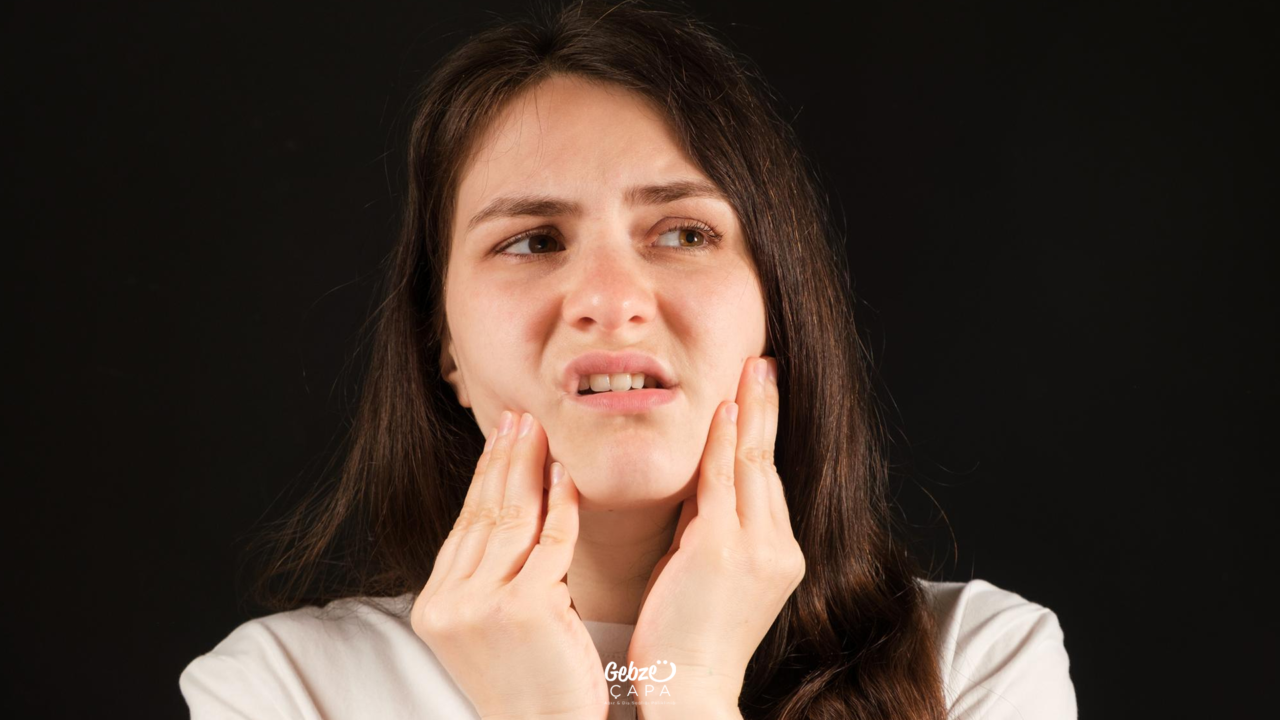

What Causes Jaw Joint Pain?
Jaw joint pain is a condition that can occur due to various factors. The main reasons are:
- Muscle Tension and Stress: Stress and anxiety experienced in daily life can cause the muscles around the jaw to tighten. This condition can disrupt the normal function of the jaw joint and cause pain.
- Joint Damage or Injury: Accidents, blows, or blows received during sports activities can damage the jaw joint, leading to pain. A traumatic impact, especially to the jawbone or joint area, can cause damage to the joint.
- Arthritis: Joint inflammations such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can cause pain and limitation of movement in the jaw joint. These conditions usually occur due to deterioration and inflammation of the cartilage tissue in the joint.
- Jaw Closure Disorders: Misalignment or poor bite (malocclusion) of the teeth can place extra stress on the jaw joint. This condition can lead to overload of the jaw joint and surrounding structures and pain over time.
- Bruxism (Teeth Clenching or Grinding): Unconsciously clenching or grinding teeth during sleep or during the day can put excessive stress on the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. This can lead to problems such as jaw joint pain and even wear on teeth.
Treatment of jaw joint pain is generally determined by the severity of the pain, its origin, and the individual’s general health status. Treatment options may include medications (painkillers, muscle relaxants), physical therapy, dietary changes (avoiding hard foods), stress management, and surgery when necessary.
Symptoms of Jaw Joint Pain
Symptoms of jaw joint pain may vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the jaw area
- Pain when chewing or talking
- Restricted movement or locking in the jaw
- Clicking or crackling sounds coming from the jaw joint
- Pain in the face, neck or shoulders
- Headaches and migraines
- Earache or ringing (tinnitus)
- Diagnosing Temporomandibular Joint Pain
Diagnosing jaw joint pain requires a detailed medical evaluation. The dentist or oral surgeon reviews the patient’s medical history, performs a physical examination, and uses imaging techniques (x-ray, MRI, or CT scans) if necessary. Special tests may also be performed to evaluate jaw joint function.
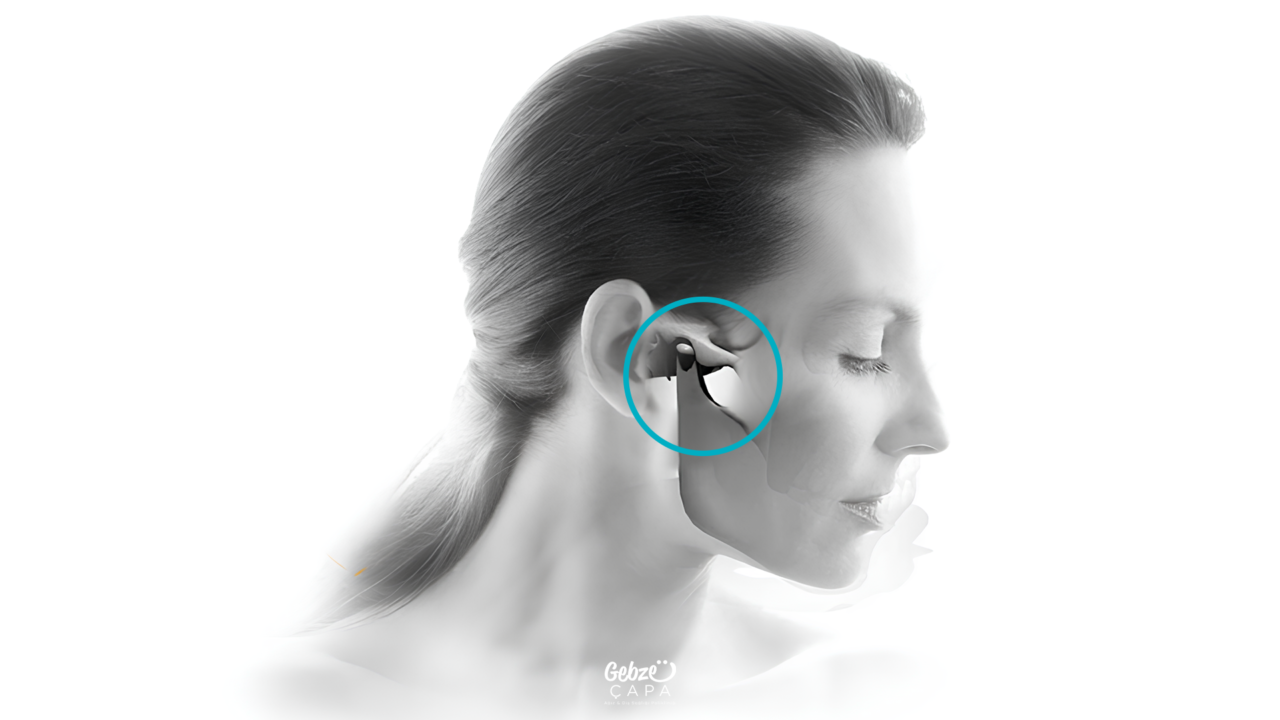
Jaw Joint Treatment
Treatment of jaw joint pain varies depending on the underlying causes and the severity of the pain. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress management, regular exercise and a healthy sleep pattern can reduce stress on the jaw joint.
- Diet Changes: Eating soft foods, avoiding chewing gum, and not taking large bites can reduce pressure on the jaw joint.
- Physical Therapy: Special exercises to strengthen and stretch the jaw muscles can improve jaw joint function.
- Medical Treatment: Painkillers, muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs can be effective in relieving pain. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may also be administered.
- Oral Appliances: The use of a night plate or splint may be recommended to prevent bruxism and protect the jaw joint.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases that do not respond to treatment, surgical intervention may be required. Procedures such as arthrocentesis, arthroscopy, or open joint surgery can relieve jaw joint pain.
To summarize: Jaw joint pain is a condition that can seriously affect the quality of daily life. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, pain and discomfort can be greatly reduced. It is important to have regular check-ups with your dentist or oral surgeon to maintain your jaw joint health. If you are experiencing jaw joint pain, you need to consult a specialist to create a correct diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, a healthy jaw joint is an important part of your overall oral health…