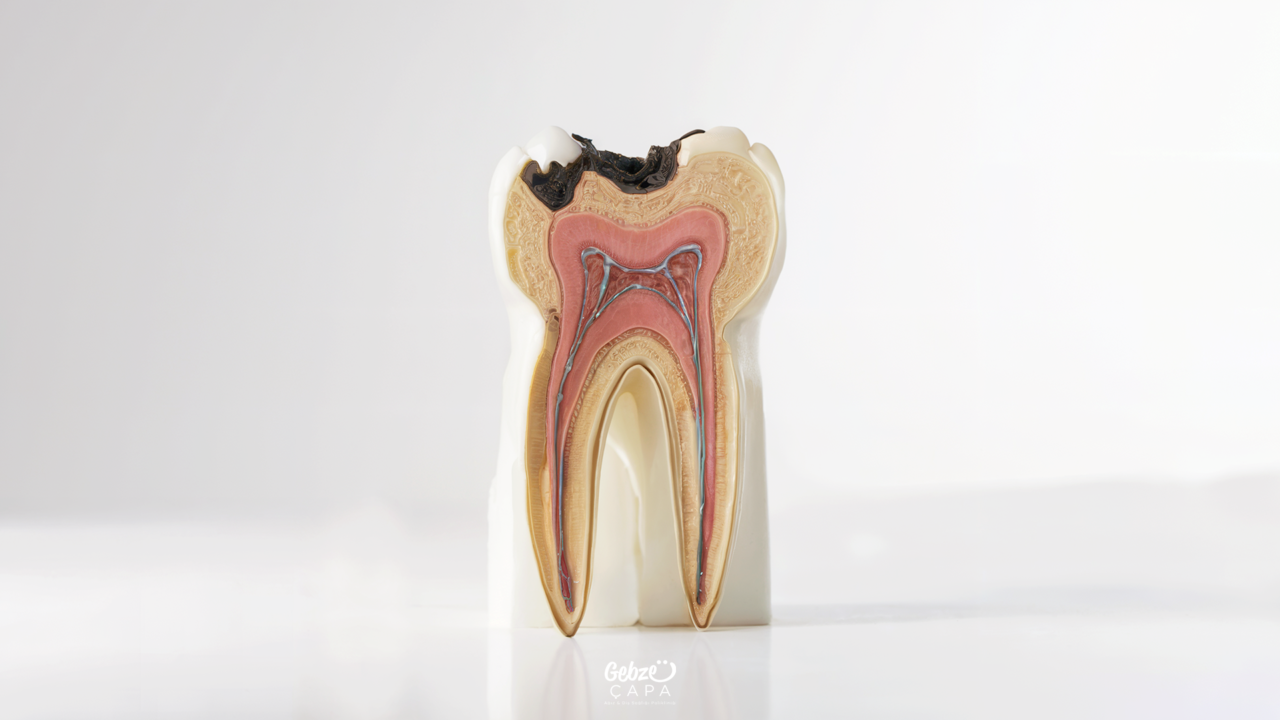
What is Dentin Caries?
Dentin caries is a type of decay that occurs in the dentin layer, which is the deeper layer of the tooth. This layer beneath the tooth enamel is softer and less mineralized, making it more susceptible to cavities. If dentin caries is not diagnosed and treated early, it can progress to the pulp (nerve) layer of the tooth and cause serious toothaches and infections.
The development of dentin caries usually begins as a result of damage or wear to the tooth enamel. Breakage or wear of tooth enamel makes it easier for bacteria to reach the dentin layer. These bacteria produce acid by breaking down organic substances in the dentin layer. These acids demineralize the dentin layer, causing the decay to spread.
Dentin decay is especially common among children and teenagers because tooth enamel is not fully mature in these age groups, making teeth more vulnerable to cavities. However, it can be seen in all age groups, and factors such as not cleaning teeth regularly, poor oral hygiene and excessive sugar consumption may increase the risk.
Causes of Dentin Caries
Dentin caries occurs when tooth enamel is damaged and bacteria reach the dentin layer. There are several main reasons for this situation:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing teeth regularly and not using dental floss leads to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria. Plaque erodes tooth enamel and reaches the dentin layer. Inadequate brushing and flossing causes bacteria to multiply and produce acid. These acids erode tooth enamel, causing the protective barrier to break down. It is important to brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day to prevent plaque buildup.
- Sugary and Acidic Foods: Foods and drinks containing sugar and acid weaken tooth enamel, making it easier for bacteria to reach dentin. Sugary foods are fermented by bacteria, leading to acid production. Acids disrupt the mineral structure of tooth enamel, paving the way for caries formation. Acidic drinks directly erode tooth enamel, weakening the protective layer. Brushing your teeth or rinsing them with water after consuming sugary and acidic foods reduces the acid effect.
- Weakening of Tooth Enamel: Weakening of tooth enamel due to reasons such as aging, genetic factors or acid erosion paves the way for dentin caries. As we age, the natural process of wear of tooth enamel begins, weakening the protective barrier of the teeth. Genetic factors can cause some individuals’ tooth enamel to be thinner and less durable. Acid erosion can occur as a result of stomach acid reflux, frequent vomiting, or excessive consumption of acidic foods and drinks. The weakening of tooth enamel makes it easier for bacteria to reach the dentin layer.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva neutralizes bacteria and acids in the mouth. When there is not enough saliva production, the risk of cavities increases. Saliva constantly washes the tooth surface, preventing plaque accumulation and maintaining oral pH balance. Dry mouth occurs when the salivary glands fail to produce enough saliva, and this condition usually develops as a side effect of some medications, dehydration, or problems with the salivary glands. Insufficient saliva production makes it difficult to neutralize acids in the mouth. To prevent dry mouth, it is useful to drink plenty of water, chew sugar-free gum and use saliva-increasing products when necessary.
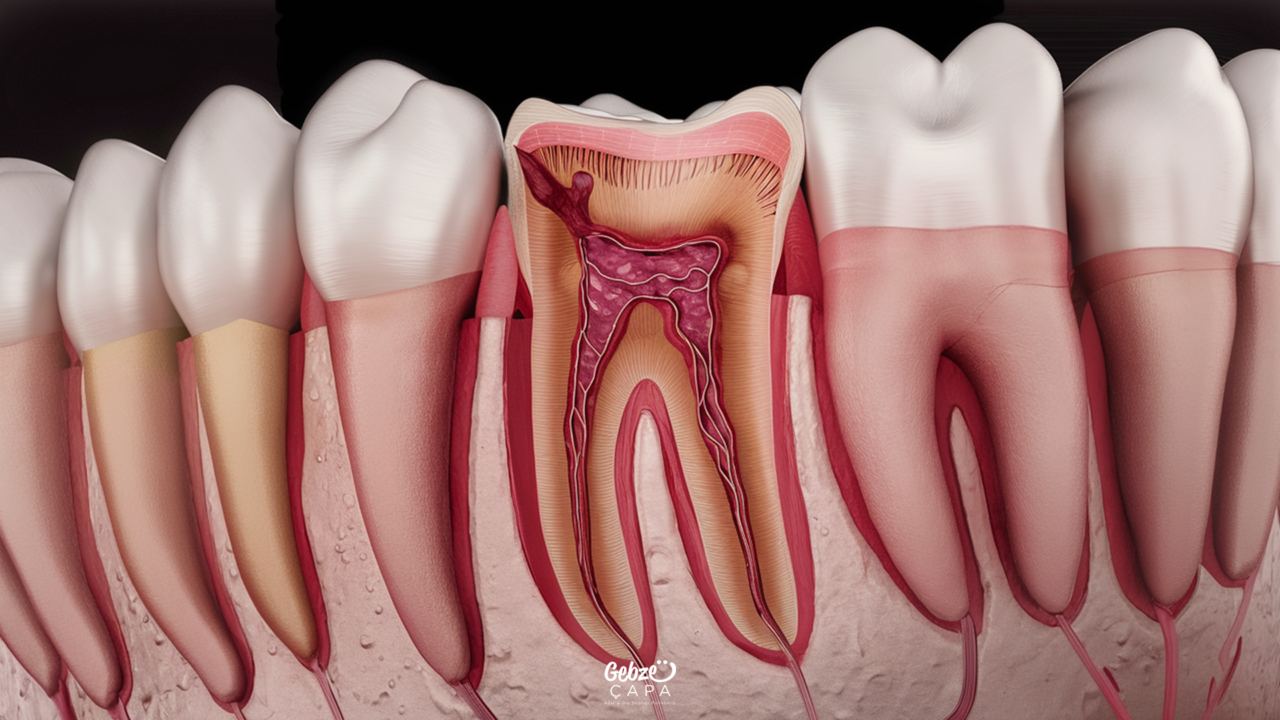
Dentin Caries Symptoms
Symptoms of dentin caries may vary depending on the stage of progression of the caries.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Sensitivity or pain is felt in the tooth when it comes into contact with hot, cold, sweet or acidic foods and drinks. This sensitivity becomes more evident, especially as the dentin layer is exposed.
- Toothache: As the decay progresses, constant or intermittent pain may occur in the tooth. These pains, which are initially mild and short-lived, may become more intense and long-lasting as the decay spreads deeper into the dentin layer.
- Discoloration: Yellowing or dark spots may appear on the tooth. Since dentin decay usually begins on the inside of the tooth, these symptoms can be noticed from the outside. The color of the tooth changes depending on the spread of caries and demineralization of the dentin layer.
- Tooth Decay: Visible cavities or holes may occur in the tooth. These holes become more visible as the decay progresses and lead to a weakening of the tooth structure. Tooth decay is more common, especially on the chewing surfaces of the teeth or in areas close to the gum line.
Dentin Caries Treatment
Treatment of dentin caries varies depending on the degree of progression of the caries. Here are the main treatment methods:
- Fluoride Treatment: In the early stages, it is possible to strengthen tooth enamel and stop the progression of decay by using products containing fluoride. Dentists can slow the progression of decay by applying fluoride gels or varnishes.
- Filling: Dentin decay usually creates cavities in the tooth. By filling these gaps with filling materials, the progression of decay is stopped and the function of the tooth is restored. Tooth fillings are made using materials such as composite resin or amalgam.
- Root Canal Treatment: If the decay has progressed to the pulp layer of the tooth, root canal treatment may be required. In this procedure, the infected pulp from the inside of the tooth is removed, cleaned and filled. The tooth is then protected by covering it with a crown.
- Crown: If the decay is very large and the structural integrity of the tooth is seriously damaged, the entire tooth can be covered with a crown. This protects the tooth, preventing further damage.
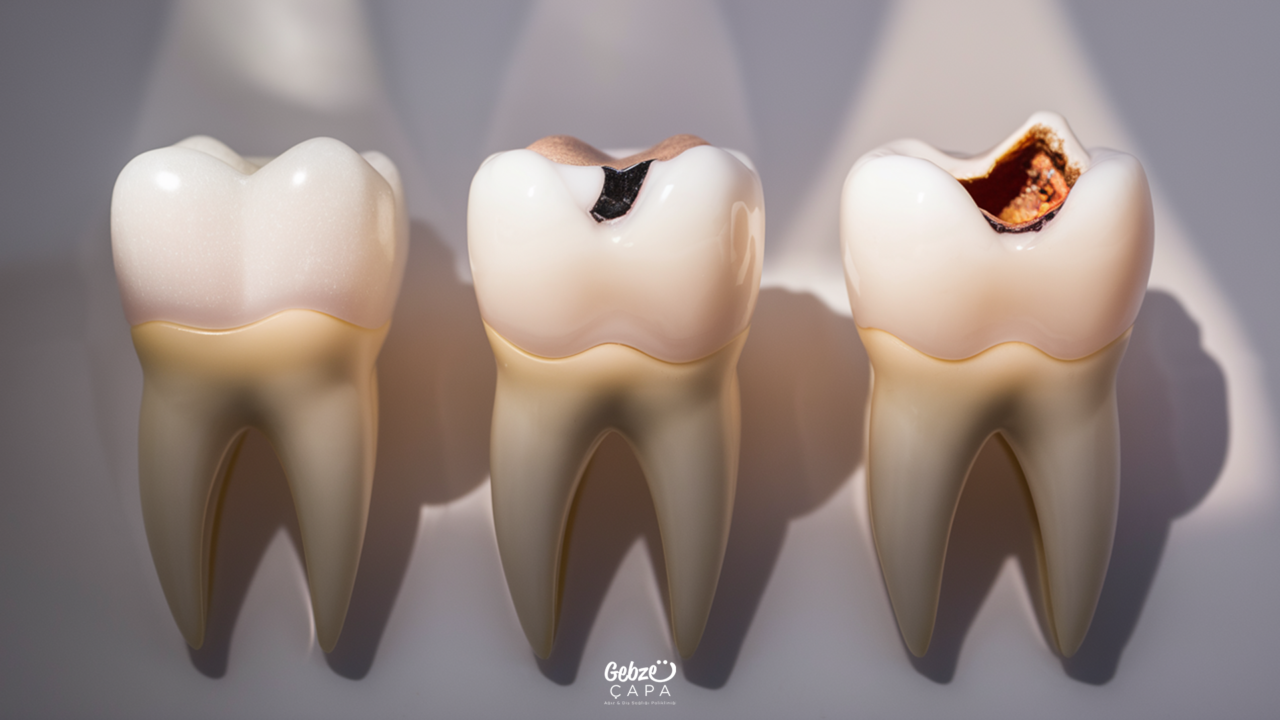
How Can We Prevent Dentin Decay?
The following steps can be followed to prevent dentin caries:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Prevent plaque buildup by brushing and flossing your teeth at least twice a day.
- Balanced Diet: Protect tooth enamel by limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Regular Dentist Check-ups: Ensure early detection of cavities by visiting your dentist regularly.
- Fluoride Use: Strengthen tooth enamel by using fluoride toothpastes and mouthwashes.
- Preventing Dry Mouth: Prevent dry mouth and stimulate saliva production by drinking adequate amounts of water.