Dental health is not limited to teeth that are free of cavities and white. The tooth root and surrounding tissues are just as important as the tooth itself. Infections, inflammations and cyst formations, especially at the root tip, can lead to tooth loss. In such cases, a special surgical method that has been used in the world of dentistry for a long time comes into play: Apical resection. So, what is apical resection?
What is Apical Resection?
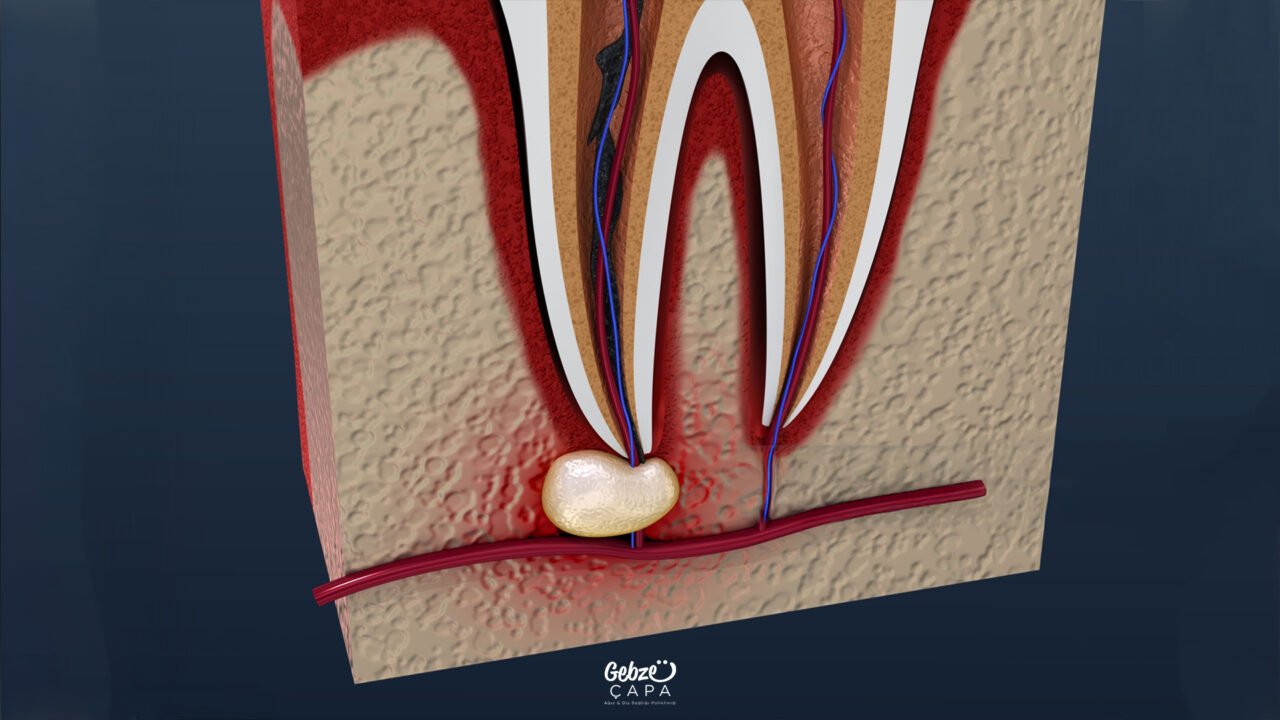
Apical resection is a surgical treatment method performed to eliminate persistent infections occurring in the tooth root. It is usually used in cases where the infection in the tooth cannot be eliminated with root canal treatment, drug treatment or other classical methods. Thanks to this procedure, infected tissues are cleaned without the need for tooth extraction and the tooth is kept in the mouth in a healthy way.
During apical resection, the infected tip of the tooth root and the inflamed tissues around it are carefully removed. After the pathological tissues in this area are completely cleaned, the tip of the root is cut and corrected and the root canal is closed with special filling materials. In this way, the source of infection is eliminated and re-inflammation of the tooth is prevented.
This procedure is also known as apicoectomy or root tip surgery as it is known among the public. Apical resection is usually applied to teeth with lesions such as cysts, granulomas or chronic inflammation at the root tip. It offers an effective solution especially in cases where previous root canal treatments have failed and infection has developed again.
Surgical application is performed under local anesthesia, meaning the patient does not feel any pain during the procedure. Before the operation, a small incision is made in the gum and the jawbone is reached. After the problematic part of the root is removed, the area is sterilized and the incision is closed with stitches. The healing process usually takes a few weeks and it is important to follow the care instructions recommended by the doctor during this period.
In Which Cases Is Apical Resection Applied?
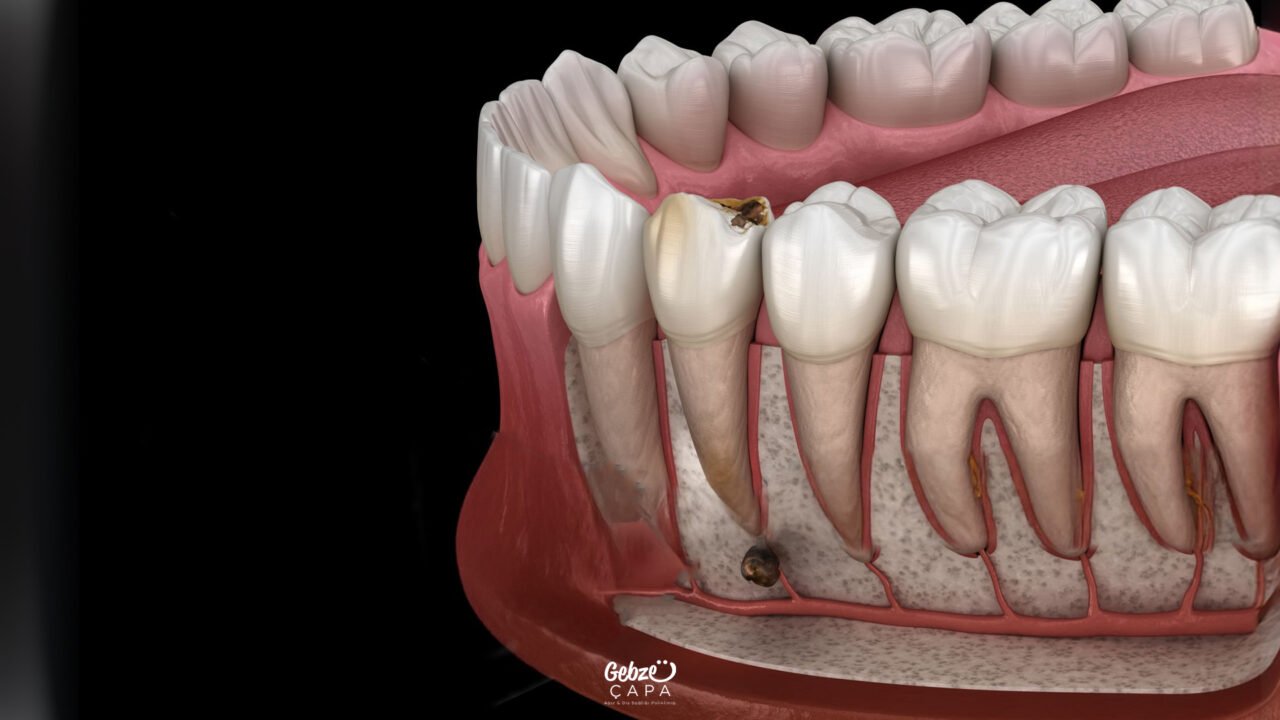
Not every tooth infection requires apical resection; this surgical procedure is preferred in certain cases. It is especially applied in cases where the infection reoccurs after root canal treatment, cysts form in the tooth root, or the canal is completely blocked and cannot be treated again. In addition, apical resection is an important option in cases of chronic inflammations that cause bone loss at the root tip, a broken instrument (such as a canal file) remaining in the canal, or in cases where healing cannot be achieved with standard canal treatment. In short, this surgical method acts as a savior to keep the tooth in the mouth in root tip problems that cannot be solved with canal treatment.
How Is Apical Resection Performed?
The apical resection procedure is performed in a completely sterile environment and under local anesthesia, ensuring that the patient does not feel any pain during the procedure. Before starting the treatment, the relevant area is carefully anesthetized, then the gum and surrounding tissues are carefully lifted to reach the tooth root. The surgeon opens a small window on the jawbone to reveal the root tip, making the infected area clearly visible. Then, the inflamed tissue, granulation tissue and cyst formation, if any, at the root tip are carefully cleaned.
After the cleaning is completed, approximately 2–3 millimeters of the root are cut and removed with special surgical instruments. After this stage, a filling material called “retrograde filling” is applied to the end of the root canal; thus, preventing the development of re-infection in the future. After all these procedures are completed, the gum is closed and the incision area is fixed with stitches. The duration of the operation usually varies between 30 and 60 minutes, and most patients can easily continue their daily lives after a short rest.
Can Apical Resection Surgery Be Applied to Every Tooth?
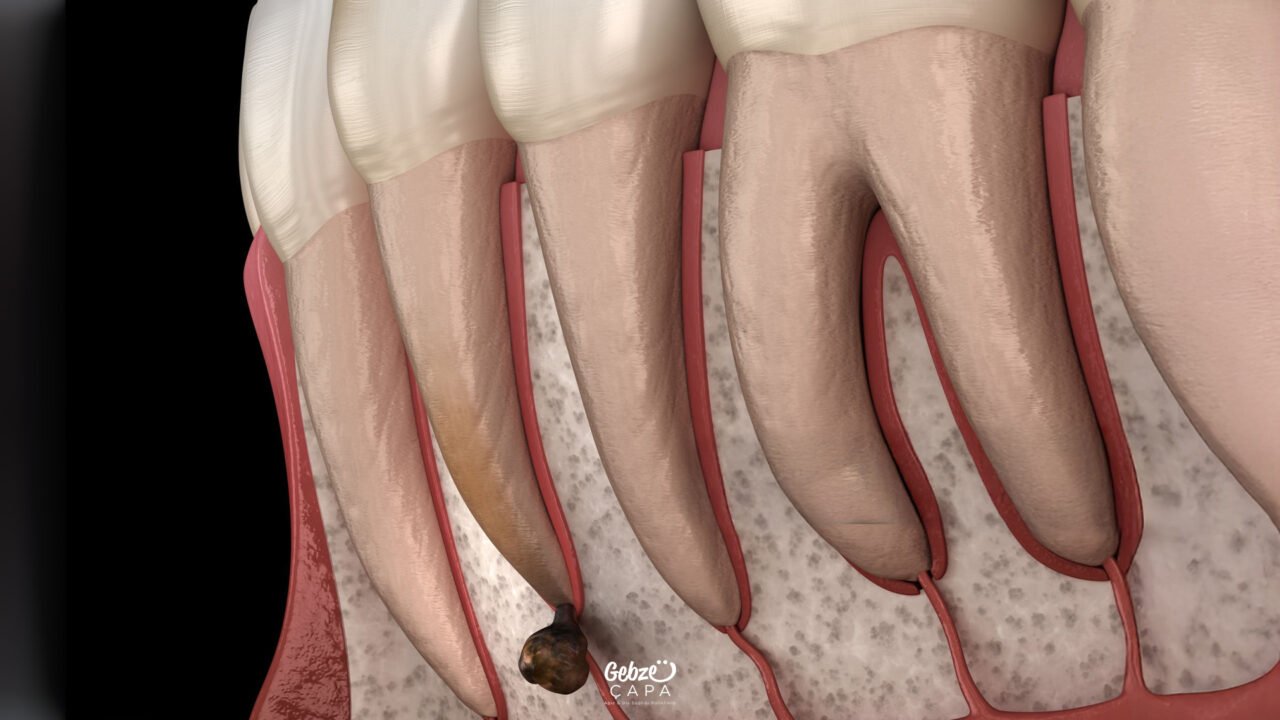
No, apical resection cannot be applied to every tooth. This procedure is most suitable for single-rooted front teeth and some premolars. Especially in molars with complex root structures and multiple roots, surgical access becomes difficult and the chance of success may decrease. In addition, if the root of the tooth is very short, the surrounding bone support is insufficient, or the tooth is severely loose, apical resection is not recommended. When making a treatment decision, the location of the tooth, root anatomy, the extent of the infection, and the tissues supporting the tooth are carefully evaluated. Therefore, a detailed examination and radiographic examination by the dentist is essential for each case.
Why We Recommend
The biggest advantage of apical resection is that it allows an infected or problematic tooth to remain healthy in the mouth instead of being extracted. In this way, the person’s chewing function is preserved and aesthetic problems due to missing teeth do not occur. In addition, jaw bone loss that may occur over time in the event of tooth loss is prevented. Thanks to this procedure, the risk of needing more costly treatments such as implants or bridges is reduced. Moreover, when planned correctly and performed by an experienced dentist, the success rate of apical resection is quite high.
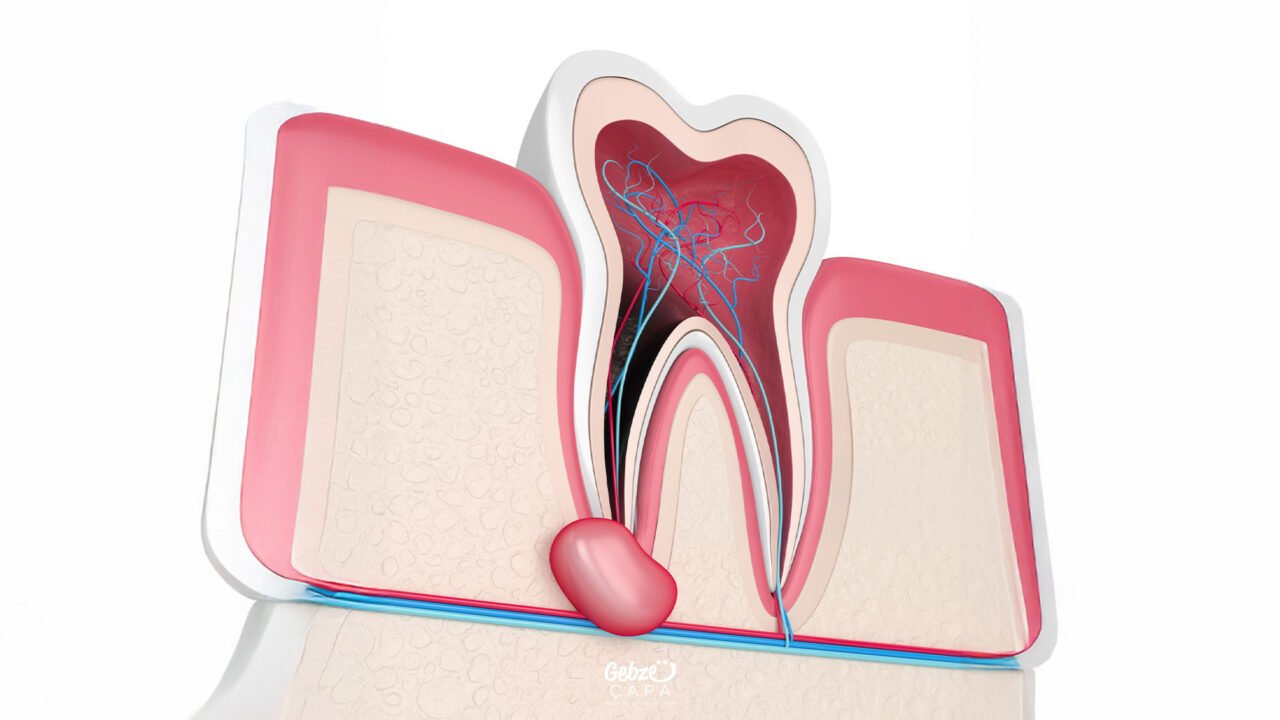
What to Consider After Apical Resection Surgery?
After apical resection surgery, your doctor will give you some important care recommendations. Applying ice to the area and resting as much as possible for 10-12 hours immediately after the procedure is very important to reduce swelling and bruising. It is completely normal for swelling to occur in the surgical area and even for the swelling to increase slightly the next day, there is no need to worry. During the recovery process, you should avoid brushing the surgical area hard, smoking, and consuming hard foods for the period specified by your doctor.
It is also not recommended to lift your lips or make excessive mouth movements to avoid straining the area where the stitches are placed, as this can cause the stitches to loosen. There may be a slight numbness in the area after the surgery; this does not mean that the nerves are damaged, it is temporary. If you experience pain, over-the-counter painkillers usually provide relief. Stitches are usually removed in 2-7 days, while the full healing process takes about 14 days. Following all these care recommendations will increase the success of the procedure and help you have a comfortable recovery period.