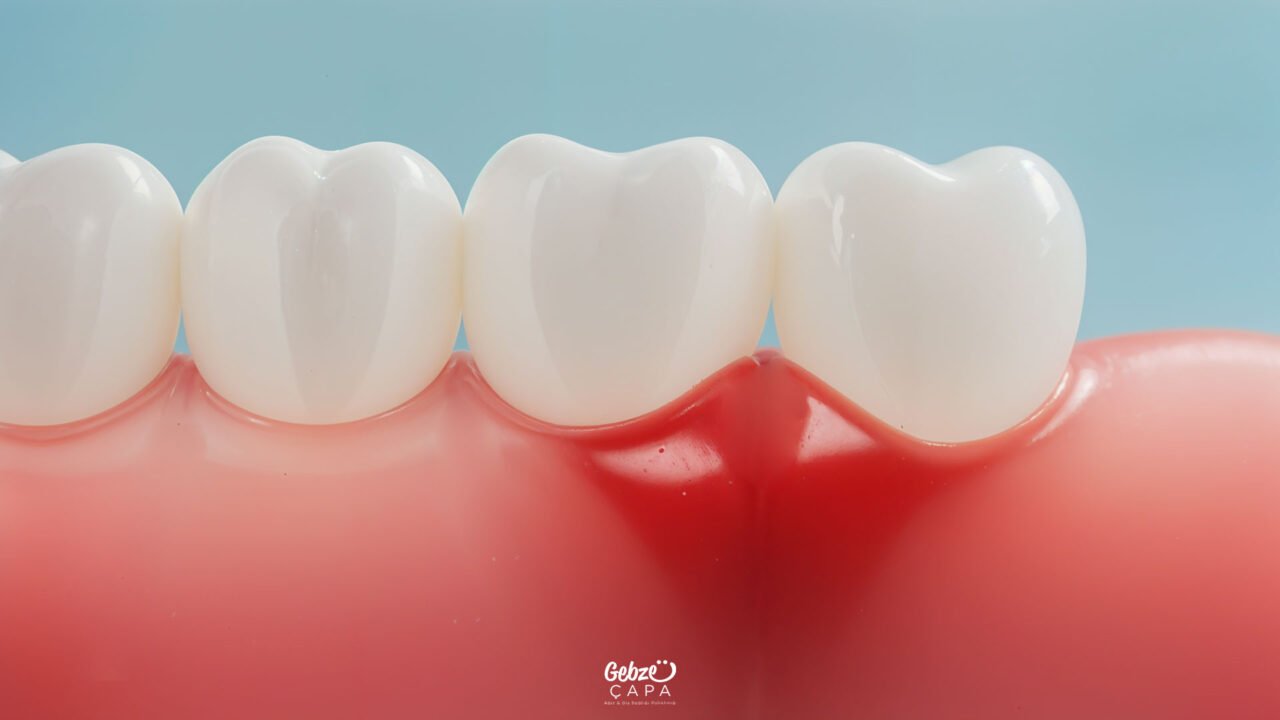
What is Gingivitis?
Oral health is a critical area that has a huge impact on overall health, and one of the most important elements in this area is the health of the gums. One of the problems that threaten the health of the gums is inflammation of the gums known as gum-boil. Gingivitis is a common problem when oral hygiene is inadequate, and if left untreated, it can lead to more serious oral and dental health problems.
Gingivitis usually manifests itself with symptoms such as redness, swelling, tenderness and bleeding in the gums. These symptoms may often be mild in the initial stages, but if left untreated, inflammation in the gums can progress and turn into periodontal disease. Periodontal diseases are among the serious conditions that affect the supporting tissues around the teeth and can lead to tooth loss.
Poor oral hygiene is the main cause of gum-boil. Not brushing your teeth regularly, not using dental floss, and neglecting oral care products cause bacterial plaque to accumulate in the mouth. These plaques can lead to inflammation of the gums and other oral health problems. Additionally, other factors such as smoking, poor nutrition, and genetic factors can also increase the risk of gingivitis.
Gingivitis Symptoms
The symptoms of gingivitis can usually be mild, but in some cases they can be quite uncomfortable and lead to serious problems. Here are the main symptoms of gingivitis and the details of these symptoms:
- Bleeding Gums: One of the most obvious and common symptoms of gingivitis is bleeding gums. Bleeding of the gums may occur when you brush your teeth or use dental floss. This bleeding may usually be small at first, but may increase over time. Bleeding gums are a sign of inflammation, usually found in the gums, indicating that the gums are inflamed and bacterial plaque has accumulated in your mouth.
- Gum Redness: Healthy gums generally have a pink and smooth appearance. However, in case of gingivitis, the gums often take on a reddish or purplish color. This redness may be a sign of inflammation and increased blood flow to the gums. Redness indicates that the gums are not in a healthy condition and are inflamed.
- Gum Swelling: Another symptom of gingivitis is swelling in the gums. Inflamed gums may be more swollen and rough than normal. Swelling indicates that bacterial plaques accumulated in the gums cause inflammation, which disrupts the natural structure of the gums. Swollen gums can cause discomfort when eating or brushing your teeth.
- Pain and Sensitivity: Gingivitis can cause pain and tenderness in the gums. You may feel pain in your gums, especially when they come into contact with hot or cold foods and drinks. This sensitivity indicates that the gums are inflamed and irritated. Discomfort may also occur when pressure is placed on the gums or when hard foods are consumed.
- Bad Breath: Gingivitis can lead to bacterial deposits in the mouth that can cause bad breath. This bad breath is usually caused by plaque and tartar that accumulates in the mouth. Bacteria can produce chemicals that cause bad breath, which can create both social and personal discomfort. Bad breath may be an indication that gingivitis is progressing and may require a review of oral care habits.
These symptoms may be a sign that something is wrong with your gums, and it is important to contact your dentist, get early treatment, and establish healthy oral hygiene habits. Once you notice the symptoms of gingivitis, you need to seek professional help and establish an effective oral care routine to prevent the condition from worsening.
Reasons
The main cause of gum-boil is a bacterial layer called plaque that accumulates on the teeth. Plaque is a layer of bacteria that forms on teeth and hardens when not cleaned regularly. Plaque can cause inflammation in the gums. Other causes of gum-boil include:
- Inadequate Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly leads to plaque accumulation.
- Smoking: Smoking negatively affects the health of the gums and increases the risk of gum-boil.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, or hormonal changes can increase the sensitivity of gums.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamin C deficiency, can affect the health of the gums.
- Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of gum diseases may be at risk of developing gum-boil.
Gingivitis Treatment
Gingivitis is generally a treatable condition, especially if it is diagnosed early. The treatment process aims to reduce inflammation of the gums and improve dental hygiene. Here are the main methods used in the treatment of gum-boil:
- Dental Hygiene: The first step in treating gum-boil is to pay attention to oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes and flossing regularly reduces plaque formation. Antibacterial mouthwashes can also be used.
- Professional Cleaning: Dentists can thoroughly clean your teeth and gums, removing plaque and tartar. This process usually involves removing tartar and improving the health of the gums.
- Dentist Checkups: Regular dentist visits are important to monitor the health of gums and teeth and intervene when necessary.
- Lifestyle Changes: If you smoke, quitting can improve the health of your gums. Additionally, a balanced diet and adequate vitamin intake also support gum health.
- Medications: In severe cases, your dentist may recommend antibiotics or antibacterial creams.
Prevention
Preventing gum-boil is a key element of maintaining oral health. Here are the precautions that can be taken to reduce the risk of gum-boil:
- Regular Tooth Brushing: Brush your teeth twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Remove plaque and food debris from between the teeth using dental floss.
- Balanced Diet: Choose a diet rich in Vitamin C and other nutrients.
- Regular Dentist Check-ups: Visit your dentist at least twice a year and have your teeth cleaned.
- Non-Smoking: Avoid or quit smoking.
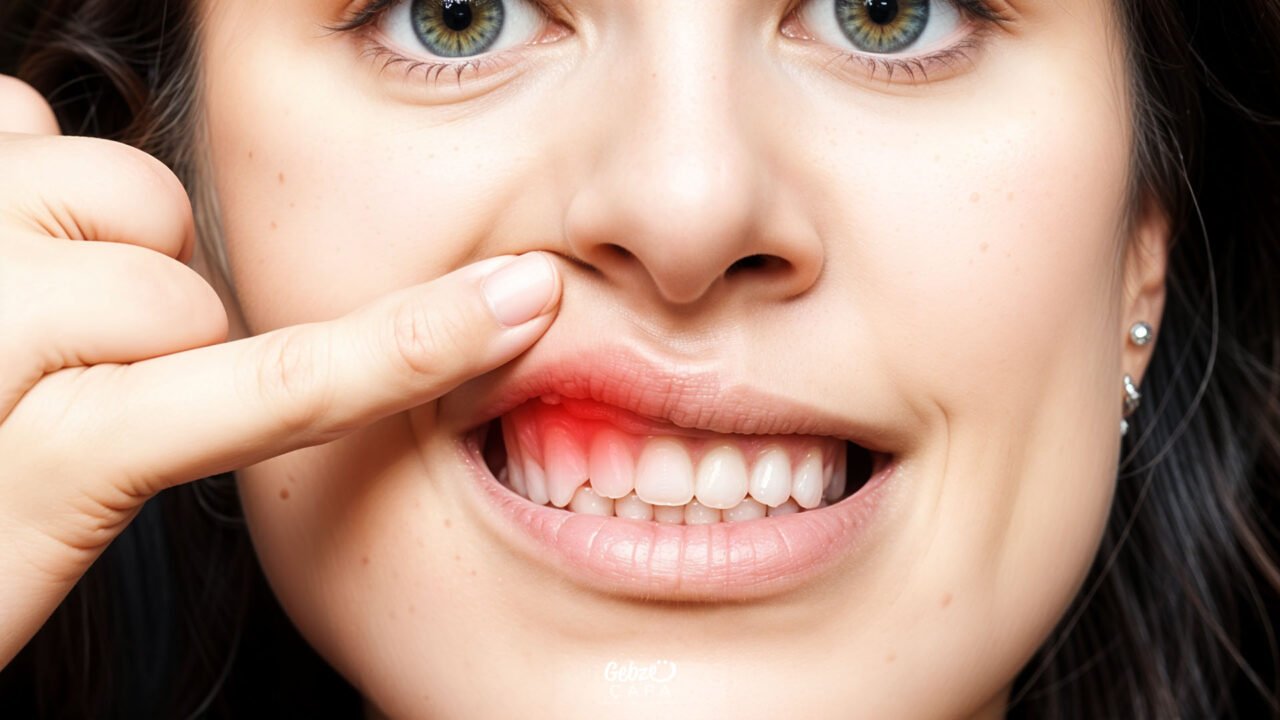
Gingivitis is a common oral health problem that causes inflammation of the gums. It is possible to regain the health of the gums with early diagnosis and treatment. Taking care of dental hygiene and regular dentist check-ups help prevent and treat gum-boil. By protecting your oral health, you can reduce the risk of developing gum disease and improve your overall health. Remember, the health of your gums is critical for your overall health, and taking the necessary precautions in this regard will benefit you greatly in the long run.